Abstract
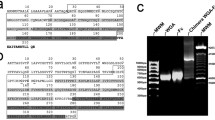
Aspergillus fumigatus is a highly pathogenic fungus causing a wide spectrum of diseases in immunocompromised as well as immunocompetent hosts. The present work was undertaken to evaluate the cytotoxic nature of fractionated antigens of A. fumigatus against the mammalian cell lines (J774, RAW, CHO and L929). An enriched protein antigenic fraction of A. fumigatus was subjected to con A Sepharose and phenyl Sepharose chromatography. Antigenic fractions, ConAub (conA unbound) and PSC III (fraction III of phenyl Sepharose column) containing low mw antigens showed higher cytotoxicity as compared to other antigenic fractions. PSC III was further purified on HPLC resulting in an 18 kDa homogeneous protein. The purified protein showed high ELISA absorbance values for specific IgG and IgE antibodies in sera of ABPA patients. Monoclonal antibody raised against Asp fl, a major allergen/antigen of A. fumigatus recognised the purified 18 kDa by ELISA and western blot. The 18 kDa allergen/antigen or Asp fl showed similar toxicity towards all the four cell lines (macrophage and fibroblast) with an IC50 of 75 ng/ml or 4.16 nM. Reduction in toxicity of 18 kDa at low temperatures and potentiation in presence of ammonium chloride and monensin indicates mechanism of internalisation of 18 kDa in eukaryotic cells is similar to α-sarcin. The present work shows that the 18 kDa allergen/antigen (Asp fl) is a major cytotoxin secreted by A. fumigatus which may play multiple roles in the pathogenesis of Aspergillosis through allergenicity, antigenicity and cytotoxicity. (Mol Cell Biochem 167: 89-97, 1997)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardana EJ Jr.: The clinical spectrum of aspergillosis. Part 2: classification of saprophytic, allergic and invasive variants of Aspergillus fumigatus. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 13: 85, 1980
Kurup VP, Kumar A: Immunodiagnosis of aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 4: 439, 1991
Kolattukudy PE, Lee JD, Rogers LM, Zimmerman P, Ceselski S, Fox B, Stein B, Copelan EA: Evidence for possible involvement of an elastinolytic serine protease in aspergillosis. Infec Immun 6: 2357, 1993
Olson BJ, Jennings JC, Roga V, Junek AJ, Shuurmans DM: Alpha-sarcin a new antitumor agent. II. Fermentation and antitumor spectrum. Appl Microbiol 13: 314, 1965
Conde FP, Orlandi R, Canevari S, Mezzanzanica D, Ripamonti M, Munoz SM, Jorge P, Colnaghi MI: The Aspergillus toxin restrictocin is a suitable cytotoxin agent for generation of immunoconjugates with monoclonal antibodies directed against human carcinoma cells. Eur J Biochem 178: 795, 1989
Fernandez-Luna JL, Lopez-Otin C, Soriano F, Mendez E: Complete aminoacid sequence of the Aspergillus cytotoxin mitogillin. Biochemistry 24: 861, 1985
Arruda LK, Platts-Mills TAE, Fox JW, Chapman MD: Aspergillus fumigatus allergen 1, a major IgE binding protein, is a member of the mitogillin family of cytotoxins. J Exp Med 172: 1529–1532, 1992
Banerjee B, Chetty A, Joshi AP, Sarma PU: Identification and partial characterisation of diagnostically relevant antigens of A. fumigatus. Asian Pac J Allergy and Immunology 18: 13–18, 1990
Banerjee B, Madan T, Sharma GL, Prasad HK, Nath I, Sarma PU: Characterisation of 45 kd glycoprotein antigen of A. fumigatus. Serodiag and Immunotherap 7, 1996, In press
Bir N: Immunochemical and biochemical characterisation of antigens of A. fumigatus. Thesis, 1996
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680, 1970
Towbin H, Stachalin T, Gordon J: Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gel to nitrocellulose sheets, procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76: 4350, 1979
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65: 55, 1983
Latge JP, Moutaouakil M, Debeaupuis JP, Bouchara JP, Haynes K, Prevost MC: The 18 kilodalton antigen secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun 59: 2586, 1991
Smith JM, Tang CM, Noorden SV, Holden DW: Virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus double mutants lacking restrictocin and an alkaline protease in a low dose model of invasive aspergillosis. Infect Immun 62: 5247, 1994
Gasset M, Onaderra M, delPozo AM, Schiavo G, Laynez J, Usobiaga P, Gavilanes JG: Effect of antitumor protein α-sarcin on the thermotropic behaviour of acid phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1068: 9, 1991
Deurs BV, Petersen OW, Olsnes S, Sandvig K: The ways of endocytosis. International Review of Cytology 117: 131, 1989
Youle RJ, Newton D, Wu Y, Gadina M, Rybak SM: Cytotoxic ribonucleases and chimeras in cancer therapy. Crit Rev Therap Drug Carrier Sys 10: 1, 1993
Arruda LK, Mann BJ, Chapman MD: Selective expression of a major allergen and cytotoxin Asp fl in A. fumigatus. J Immunol 149: 3354–3359, 1992
Endo Y, Huber PW, Wool IG: The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha sarcin. J Biol Chem 258: 2662, 1982
Orlandi R, Canevari S, Conde FP, Leoni F, Mezzanzenica D, Colnaghi MI: Immunoconjugate generation between the ribosome inactivating protein restrictocin and antihuman breast carcinoma MAB. Cancer Immunol Immunother 26: 114, 1988
Pai LH, Pastan l: Immunotoxins and recombinant toxins for cancer treatment. Important advances in oncology. In: Vincent T DeVita, Samuel Hellman and Steven A Rosenberg (eds). JB Lippincott Company, Philadelphia 1994, p 3
Vitetta ES, Thorpe PE, Uhr JW: Immunotoxins: magic bullets or misguided missiles? TiPS 14: 148, 1993
Jin FS, Youle RJ, Johnson VG, Shiloach J, Fass R, Londo DL, Bridges SH: Suppression of the immune response to immunotoxins with anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 146: 1806, 1991
Roga V, Hedeman LP, Olson BH: Evaluation of mitogillin (NSC-69529) in the treatment of naturally occurring canine neoplasms. Cancer Chemother Rep Part 1 55: 101, 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madan, T., Arora, N. & Sarma, P.U. Identification and evaluation of a major cytotoxin of A. fumigatus. Mol Cell Biochem 167, 89–97 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006823706119
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006823706119